Layout Containers
Author: Gu Zhu
When creating UI that adapts to different screen resolutions, layout containers are another commonly used method besides the relational system. Layout containers typically refer to GBox, but derived classes such as GPanel and GList have similar functionality.
1. Editor Operations
(Figure 1-1)
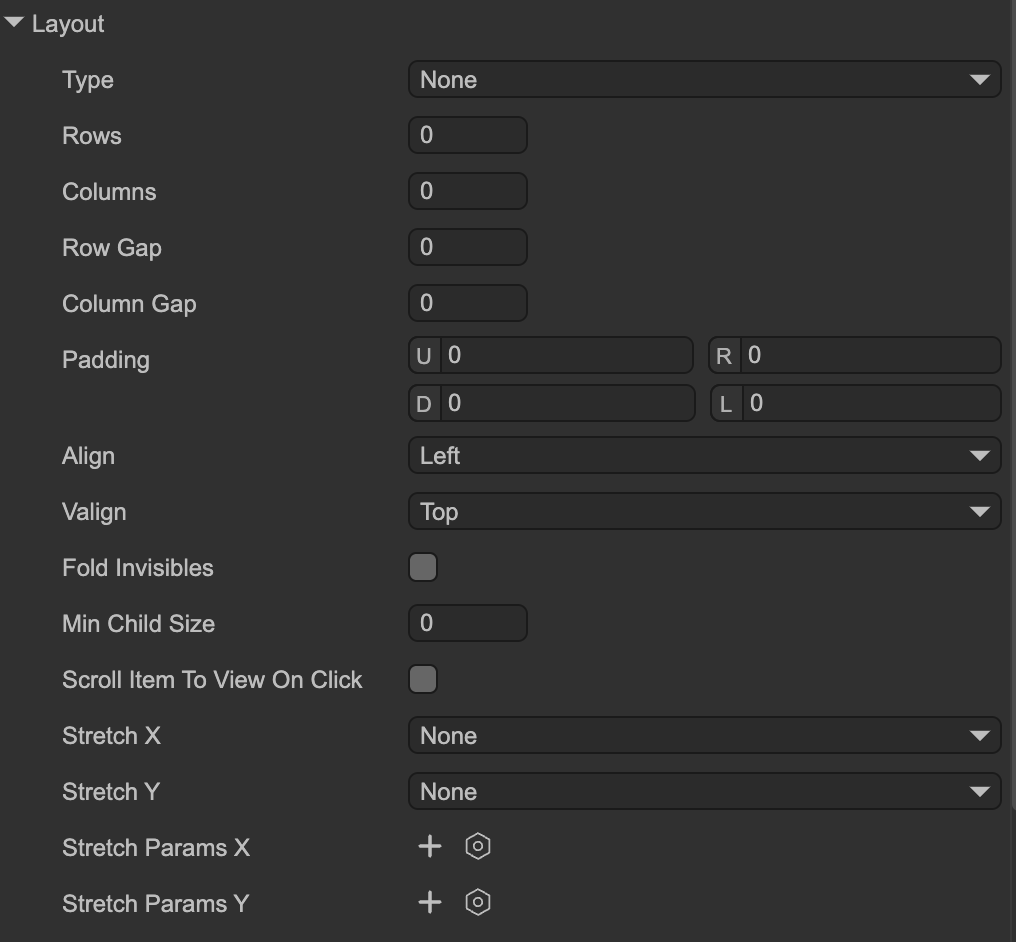
Layout Properties
Type: Layout type
None– No layout. Child nodes maintain their original position and size.Single Column– One item per row, vertically arranged.Single Row– One item per column, horizontally arranged.FlowX– Items are arranged horizontally. When reaching the right edge of the viewport or a specified number of columns, it wraps to a new row.FlowY– Items are arranged vertically. When reaching the bottom of the viewport or a specified number of rows, it wraps to a new column.
- Rows: Only applicable to
FlowYlayouts. If set to a value > 0, a new column starts after this many items. - Columns: Only applicable to
FlowXlayouts. If set to a value > 0, a new row starts after this many items. - Row Gap: Distance between rows. Can be negative.
- Column Gap: Distance between columns. Can be negative.
- Padding: Set internal padding on all four sides of the container.
- Align: Horizontal alignment of items.
- Valign: Vertical alignment of items.
- Fold Invisibles: If checked, invisible items (
visible=false) are ignored in the layout and occupy no space. If unchecked, space is reserved for invisible items, resulting in blank placeholders. - Min Child Size: When automatically resizing child nodes based on layout, their size will not be smaller than this value. For example, if set to 30 and a node’s calculated width is 10, it will be adjusted to 30.
- Scroll Item To View On Click: If checked, clicking an item partially visible in the viewport will automatically scroll it fully into view.
Stretch X: Horizontal stretching behavior:
None– No stretching; item width remains unchanged.Stretch– Scale items to fill the viewport width. For example, in aSingle Columnlayout (one item per row), the item’s width becomes the viewport width.Resize to Fit– Adjust viewport width to fit the maximum width of all items horizontally. The item widths remain unchanged.
- Stretch Y: Vertical stretching behavior. Same as
Stretch Xbut for height. Stretch Params X: Parameters for horizontal stretching. An array where each element corresponds to a column in order. Note that invisible columns due to
Fold Invisiblesare skipped in alignment.Ratio– Proportional width for the column. For example, 0.5 means the column occupies 50% of the available width.Priority– Determines which items adjust first when width exceeds or is insufficient. Runtime values are normalized to -1, 0, or 1.Min– Minimum width of items in this column.Max– Maximum width of items in this column.Fixed– Column width is fixed; item widths remain unchanged.
- Stretch Params Y: Parameters for vertical stretching. Same as
Stretch Params Xbut for height.
2. Common API
When layout properties change, the container is automatically marked as dirty and refreshed before the next render. Exception: when modifying stretchParamsX or stretchParamsY, you must manually mark the layout as changed:
// No need to manually mark as dirty
aBox.layout.foldInvisibles = true;
// Manual dirty flag required
aBox.layout.stretchParams.push(new StretchParam().setRatio(0.5));
aBox.setLayoutChangedFlag();
aBox.layout.stretchParamsX[0].ratio = 0.8;
aBox.setLayoutChangedFlag();
The container automatically refreshes layout positions when child nodes’ positions, sizes, visibility change, or when children are added/removed. If you need to immediately access the correct coordinates of items:
aBox.layout.refresh();